The food processing industry is a dynamic sector constantly striving for efficiency, precision, and hygiene. From milling grains to filling containers, intricate machinery plays a crucial role in every stage. At the heart of many food processing applications lies the gear reducer, a vital component responsible for modifying speed and torque – often a critical function for achieving desired processing outcomes. This article provides an in-depth analysis of gear reducer principles, examines various types suited for food processing, and compares their performance characteristics, especially considering the current trends of automation and sustainability shaping the industry. Furthermore, we'll highlight how innovative solutions like those offered by MES-Drive are addressing the evolving needs of this demanding sector.
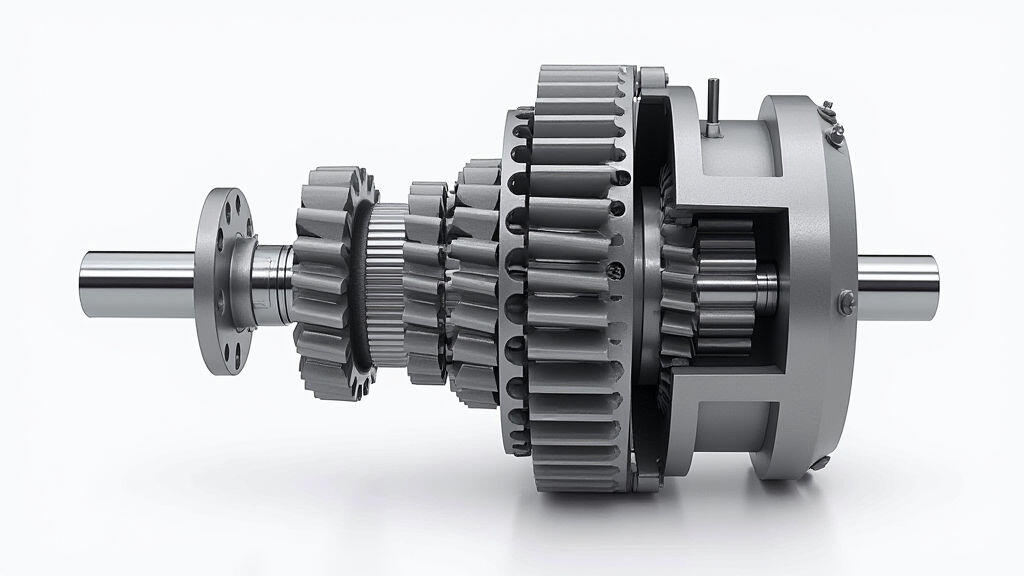
At its core, a gear reducer is a mechanical device that reduces the speed of a rotating input and increases its torque. This is achieved through the interaction of two or more gears with different sizes. The ratio between the number of teeth on the input and output gears determines the speed reduction and torque multiplication. The basic principle relies on the conservation of energy. While speed is reduced, torque is proportionally increased (ideally, neglecting frictional losses).
There are primarily three types of gear reducers found in food processing applications:

The food processing industry faces stringent requirements concerning cleanliness, hygiene, and often, compliance with regulations like HACCP. Therefore, the selection of the appropriate gear reducer is paramount.
1. Spur Gear Reducers: Generally suitable for applications where high efficiency and cost-effectiveness are prioritized. They are commonly used in processing equipment like conveyors, mixers, and grinders where precise torque transfer is needed. However, their noisier operation might be a disadvantage in certain environments.
2. Helical Gear Reducers: An excellent choice for applications where quiet operation and reduced vibration are critical. They’re frequently used in packaging machinery, filling machines, and conveying systems that operate for extended periods. The angled teeth allow for smoother power transmission and a quieter working environment, minimizing noise pollution within the facility.
3. Planetary Gear Reducers: These offer a high power density, meaning they pack a lot of power into a small space. They have become increasingly popular in modern food processing equipment, particularly in automated systems and those requiring space-saving designs. They are known for their compactness, high efficiency, and robust construction, making them suitable for high-demand applications like robotic arms and high-speed food processing lines. They also offer excellent load distribution, increasing reliability.
Evaluating the performance of gear reducers in the food processing industry requires consideration of several crucial factors:
Efficiency: Higher efficiency translates to lower energy consumption and reduced operating costs. Helical and planetary gear reducers typically offer better efficiency than spur gear reducers. The current trend towards energy efficiency is further driving the adoption of these higher-efficiency options.
Noise Level: Controlled noise is essential in food processing facilities to protect employee hearing and adhere to environmental regulations. Helical gear reducers are generally quieter.
Hygiene: Food processing equipment demands easy cleaning and sanitation. Gear reducers should be designed with smooth surfaces, sealed units, and material choices (stainless steel being the preferred option) to prevent food contamination. Powder coating is avoiding as it can generate particles during cleaning.
Durability & Reliability: Food processing equipment operates continuously and often under demanding conditions. Gear reducers need to be designed for long life and reliability, resisting wear and tear caused by frequent starts/stops, high loads, and varying operating temperatures.
Maintenance: Reduced maintenance requirements translate into lower operational costs and downtime. Sealed gear reducers with robust bearing designs require minimal maintenance.
The food processing industry is rapidly embracing automation to improve efficiency, reduce labor costs, and enhance product quality. Automation drives the need for gear reducers that offer precise speed and torque control. This is where advancements in design and manufacturing are making a significant impact. Precision gear reducers, often incorporating features like harmonic drives or advanced planetary gear designs, are becoming essential for robotic applications, automated filling systems, and precise dispensing equipment. MES-Drive has been at the forefront of designing gear reducers specifically tailored for these high-precision applications. Their offerings are engineered to match the demands of robotic systems used in food handling and packaging, ensuring accuracy and repeatability.
Beyond efficiency, sustainability is gaining increasing importance. Food processing companies are looking for ways to reduce their environmental footprint. Gear reducers play a role by optimizing energy consumption and improving the overall efficiency of processing equipment. Furthermore, MES-Drive is focusing on using high-quality, durable materials to extend the lifespan of their reducers, reducing the need for frequent replacements and minimizing waste. They are also exploring the use of eco-friendly lubricants.
In conclusion, gear reducers are indispensable components in the food processing industry, with the choice of type significantly impacting performance, efficiency, and overall operational costs. Spur gears offer cost-effectiveness, helical gears provide quiet operation, and planetary gears deliver high power density and compactness. As the industry continues to embrace automation and sustainability, the demand for high-precision, energy-efficient, and reliable gear reducers is growing. Companies like MES-Drive are innovating to meet these evolving needs, offering tailored solutions that empower food processors to optimize their operations, reduce their environmental impact, and maintain the highest standards of hygiene and quality. MES-Drive's commitment to quality, precision, and sustainable manufacturing positions them as a key partner for food processing companies striving for a competitive edge in the modern market. With the increasing adoption of AI-powered manufacturing and predictive maintenance, gear reducers like those offered by MES-Drive are poised to play an even more critical role in shaping the future of the food processing landscape.
Leave A Reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fiels are marked